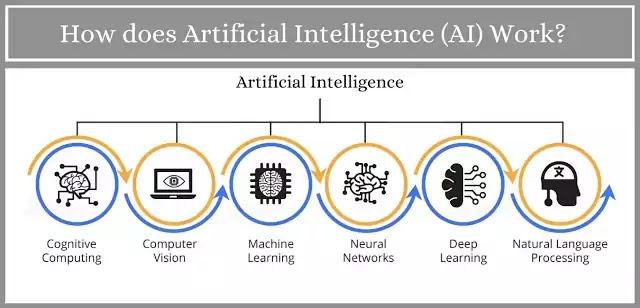
How Does AI Work? : In the rapidly advancing landscape of technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing the way we interact with machines and process information. From virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles, AI has become an integral part of our daily lives. But have you ever wondered how AI works its magic? In this article, we will delve into the underlying mechanisms that power AI systems and enable them to mimic human-like intelligence.
Data as the Foundation: At the core of AI lies data, vast amounts of it. AI systems are trained on massive datasets, allowing them to learn patterns, associations, and correlations. This training data serves as the foundation upon which AI algorithms build their understanding of the world.
Machine Learning: One of the key components of AI is Machine Learning (ML), a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms capable of learning from data. ML algorithms use statistical techniques to enable systems to improve their performance on a specific task over time, without being explicitly programmed.
a. Supervised Learning: In supervised learning, the AI model is trained on labeled data, where the input data is paired with corresponding output labels. The algorithm learns to map inputs to outputs by identifying patterns and relationships.
b. Unsupervised Learning: Unsupervised learning involves training an AI model on unlabeled data. The system must find patterns and relationships within the data without predefined output labels.
c. Reinforcement Learning: Inspired by behavioral psychology, reinforcement learning involves training AI models through a system of rewards and punishments. The algorithm learns to make decisions by maximizing cumulative rewards over time.
Neural Networks: Many AI models, especially those in deep learning, are built on artificial neural networks inspired by the structure of the human brain. These networks consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process and transform information. Deep learning models, with multiple hidden layers, can learn intricate representations of data.
Training and Optimization: During the training phase, AI models adjust their internal parameters to minimize the difference between predicted and actual outcomes. This process involves optimization techniques to fine-tune the model for better accuracy and generalization.
Inference and Decision Making: Once trained, AI models move into the inference phase, where they make predictions or decisions based on new, unseen data. This is the stage where AI demonstrates its ability to generalize from the training data to real-world scenarios.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision: AI extends its reach into understanding human language and visual data through NLP and computer vision. NLP allows machines to comprehend and generate human-like text, while computer vision enables the interpretation of visual information, opening doors to applications like image recognition and autonomous vehicles.
In conclusion, AI operates at the intersection of data, algorithms, and computational power. Through the marvels of machine learning, neural networks, and advanced algorithms, AI systems are capable of learning, adapting, and making decisions in ways that were once thought to be exclusive to human intelligence. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on various industries and aspects of our lives is poised to grow, shaping a future where intelligent machines collaborate seamlessly with humanity.