Garbage trucks, also known as waste collection vehicles, play a crucial role in maintaining the cleanliness and sanitation of urban and suburban areas. These specialized vehicles are designed to efficiently collect and transport various types of waste from residential, commercial, and industrial areas to disposal or recycling facilities. This article will provide a detailed exploration of the inner workings of garbage trucks, shedding light on their components, mechanisms, and operational processes.
Types of Garbage Trucks
Front Loader Trucks: These trucks are equipped with a hydraulic arm at the front that lifts and empties large waste containers into the truck’s hopper.
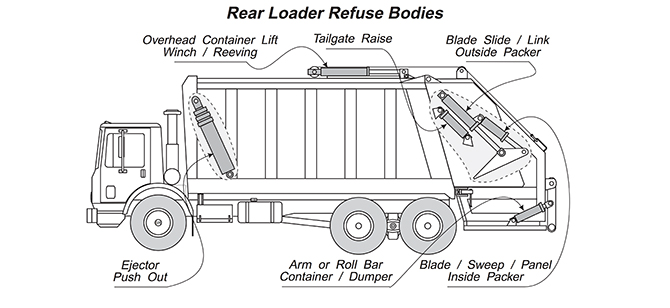
Rear Loader Trucks: These trucks feature a compactor mechanism at the rear, which compresses and stores waste in the truck’s body.
Side Loader Trucks: Fitted with a mechanical arm on the side, these trucks collect waste from curbside containers.
Collection Mechanisms
Hydraulic Systems: Most garbage trucks utilize hydraulic systems to power lifting mechanisms. Hydraulic cylinders and pumps are employed to lift and empty containers into the truck.
Compactor Units: Rear loader trucks employ compactors to compress and consolidate waste, maximizing the truck’s capacity and reducing the frequency of unloading.
Components of a Garbage Truck
Hopper: The hopper is the opening at the top of the truck where waste is deposited. It can be covered to prevent littering during transportation.
Compactor Blade: Found in rear loader trucks, the compactor blade compresses waste, creating more space and facilitating efficient collection.
Hydraulic System: This includes hydraulic cylinders, pumps, and valves that power the lifting and compaction mechanisms.
Storage Area: The body of the truck serves as a storage compartment for compacted waste, and it may have partitions for different types of waste.
Operational Process:
Collection: Garbage trucks follow a predetermined route, stopping at designated collection points. The collection process involves lifting, emptying, and compacting waste.
Transportation: Once the waste is collected, the garbage truck transports it to a designated disposal facility or recycling center.
Unloading: At the disposal facility, the truck unloads the waste, either through tipping mechanisms or by opening the rear door of the compactor.
Safety Features:
Backup Cameras: To assist drivers in navigating tight spaces and avoiding obstacles.
Warning Systems: Audible and visual warnings alert pedestrians and other vehicles to the truck’s presence.
Automatic Shutdown: Some trucks are equipped with automatic shutdown systems to prevent accidents during maintenance or emergencies.
Environmental Considerations
Emission Controls: Garbage trucks may be equipped with emission control systems to reduce their environmental impact.
Alternative Fuels: Some municipalities are exploring the use of alternative fuels, such as compressed natural gas or electric power, to make garbage trucks more eco-friendly.
Garbage trucks are essential for maintaining clean and healthy communities. Understanding their intricate workings, from hydraulic systems to compactors, provides insight into the efficiency and complexity of waste collection processes. As technology continues to advance, the evolution of garbage trucks will likely focus on increased sustainability and reduced environmental impact.






 If you want to use your preferred UPI app, our UPI ID is raj0nly@UPI (you can also scan the QR Code below to make a payment to this ID.
If you want to use your preferred UPI app, our UPI ID is raj0nly@UPI (you can also scan the QR Code below to make a payment to this ID.